3 Primary Steps in Neural Communication
Neural Impluse Receptor Sites. They communicate through action potentials which are electrical impulses that are short-lasting and send signals from one neuron to another.

Neural Communication Transmission Of The Nerve Signal Between Two Neurons With Axon And Synapse Close Up Of A Chemical Chemical Synapse Neurons Transmission
- release of neurotransmitters.
. Action potential generated near the soma. The synapses axons and dendrites all work together to create this system of communication. The basic building block of the nervous system.
- When the cell membrane becomes depolarized Potassium automatically leaves the cell until the cell is back into complete resting stage. Largest part of a typical neuron. Lastly the vesicular membrane in the neurons plasma membrane re-seals itself.
What are the 3 primary steps in neural communication. Abstract Understanding how. Students read and record results of three consecutive drops.
The action potential is an all-or-none phenomenon. Newcastle upon Tyne NE1 7R U UK. The pre-synaptic neuron talks to the post synaptic neuron at the synapse.
Travels very fast down the axon. Then the postsynaptic potentials either open or close. The brain is organized into a.
- neurotransmitters bind to receptors. - action potential generated. Your own words summarize each step including 2 key concepts or structures in each step.
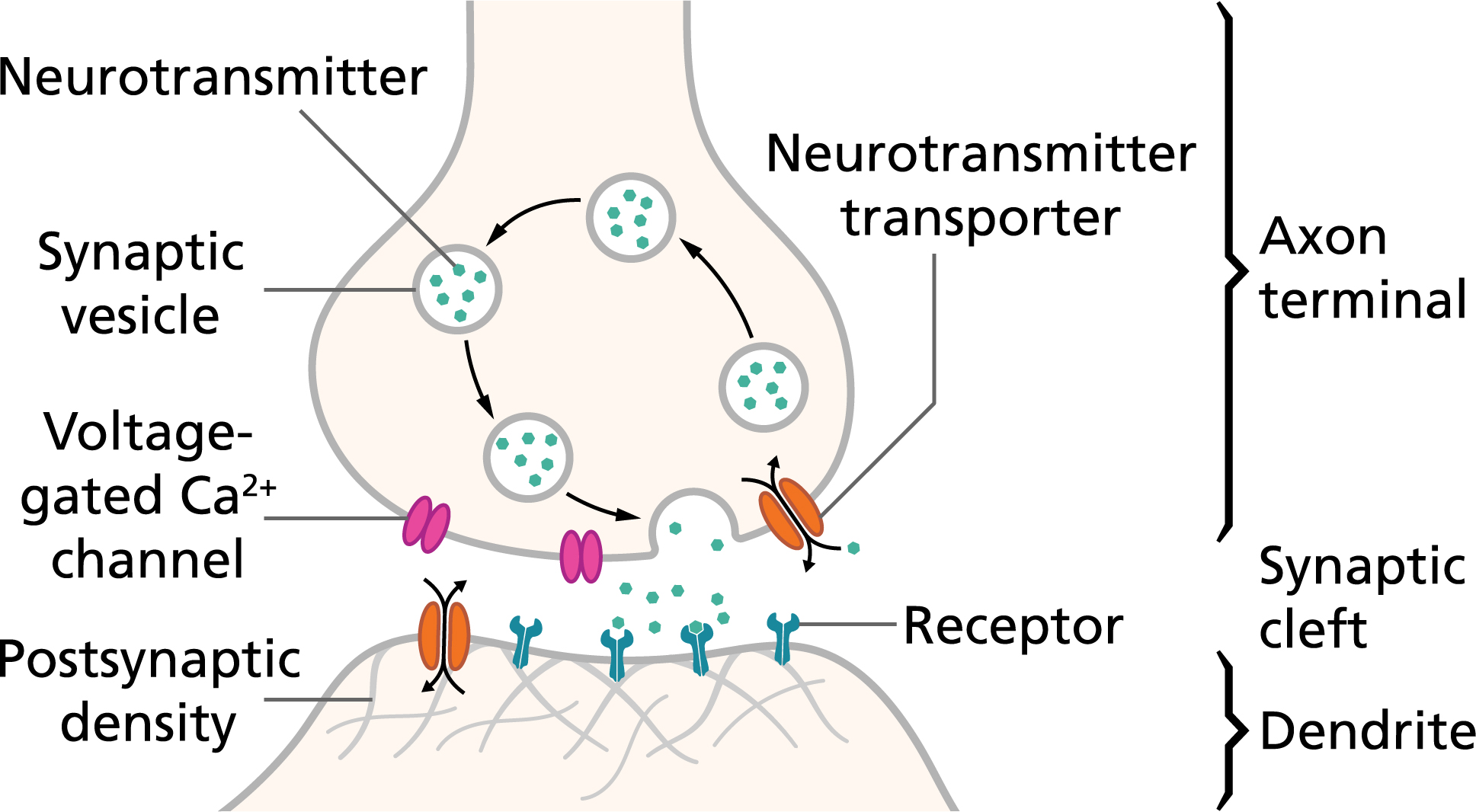
1 depolarization of the terminal membrane 2 activation of voltage-gated Ca2channels 3 Ca2entry 4 a change in the conformation of docking proteins 5 fusion of the vesicle to the plasma membrane with subsequent. Neural communication is vital for the central and. Neurons are small cells that reside throughout the human body.
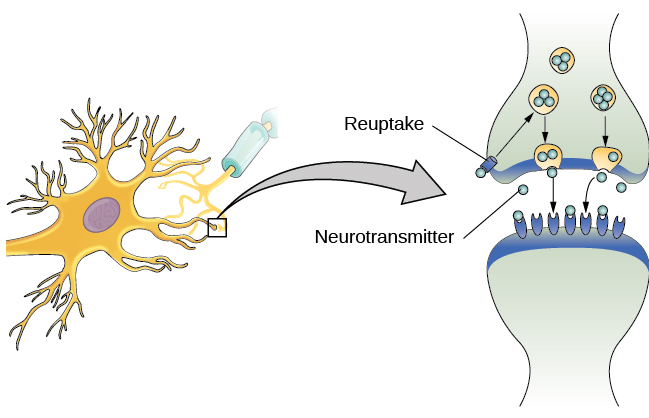
Note in the diagram above the 3 primary steps in neural communication. School of Comput ing Science. Neurotransmitters flow into the synaptic cleft.
Six Steps- Nerve Signal Conduction STEP 5. So the steps in generating action potential. Opens Voltage Gated Calcium Channels.
Dendrites receive information from a given stimulus pass it through the axon and to the synapse which then transfers that information to another neuron until all information ends up in your brain. The embryonic ectoderm which is located on the dorsal surface of the embryo is subdivided into neural ectoderm and surface ectoderm. The extension of a neuron ending in branching terminal fibers.
Steps in the basic mechanism. The membrane is depolarized by the arrival of AP. 2 neurotransmitters bind w receptors on postsynaptic neurons dendrites.
- vesicle fuses to pre-synaptic membrane. Neural communication is any type of signaling between neurons throughout the nervous system. Neurotransmitters released into synaptic cleft by presynaptic neuron.
In simple terms this means that an incoming signal from another neuron is either sufficient or insufficient to reach the. Steps for Neural Communication. The process of neural communication begins of course when a neuron receives a signal from a sending neuron via neurotransmitters.
Learn How Neurons Communicate. These neurotransmitters affect the postsynaptic membrane via a set of processes and ultimately result in changes in the permeability of the cell membrane to the important ions mentioned previously. - ions flow through the open receptor.
Researchers are proposing a new model to explain how neural networks in different brain areas communicate with each other. Second student then repeats the catch process and records results. The process of neural communication is explained in the following video.
3 excitatory inhibitory messages compared in cell body of postsynaptic neuron. The three germ layers are responsible for forming all tissues within the body. Communication between neural networks.
- A nerve cell is stimulated. Hyperpolarizing are called INHIBITORY POSTSYNAPTIC POTENTIALS IPSPs the ionic basis of postsynaptic potentials is considered under neurotransmission. If the axon reaches -55mV this opens up voltage gates ion channels initiating an action potential.
The action potential causes. Vesicles fuse with the pre-synaptic membrane. End plate potentials EPPs occur in.
After that the postsynaptic current causes either an inhibitive or excitatory postsynaptic potential which changes the excitability level of the postsynaptic cell. The fate of each layer is as follows. Describe ex-periment and decide on procedures as a class.
Step 2 -- In Response. Student pairs take turns dropping and catching the ruler. Terms in this set 8 1.
A brief electrical charge that travels down. Back out to restore the original distribution of these ions. There is another type of receptor - metabotrophic receptor.
TRANSMISSION ACROSS THE SYNAPSE. You can view the transcript for Lights Camera Action Potentials here opens in new window. Step 3 -- Response.
An action potential travels down the axon to the axon terminal. Contains the nucleus and muc. The neural ectoderm will give rise to the sensory organs eyes internal ears.
Step 1 -- Response. As they fuse they release their contents neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitter releasefrom the presynaptic terminal consists of a series of intricate steps.
All perceptions thoughts and behaviors result from combinations of signals among neurons. Communication between neurons is strengthened or weakened by an individuals activities such as exercise stress and drug use. Lots of Na entering at multiple synapses simultaneously in rapid fire sequence at one synapse.
The pump moves K back into cell and Na. Depolarizing are called EXCITATORY POSTSYNAPTIC POTENTIALS EPSPs. Calcium enters and trigger release of NT bound in synaptic vesicles.
4 1 The Neuron Is The Building Block Of The Nervous System Introduction To Psychology 1st Canadian Edition

Neural Communication Introduction To Psychology
Action Potentials And Synapses Queensland Brain Institute University Of Queensland
No comments for "3 Primary Steps in Neural Communication"
Post a Comment